How To Find K Constant In Rate Law

Rate Laws from Rate Versus Concentration Data (Differential Rate Laws)
A differential rate law is an equation of the course
![]()
In club to determine a rate law nosotros need to discover the values of the exponents northward, m, and p, and the value of the rate constant, thou.
- Determining n, m, and p from reaction orders
- Determining due north, m, and p from initial rate data
- Determining the charge per unit abiding
Determining Exponents for a Rate Law from Reaction Orders
If we are given the reaction orders for a reaction, we have the values of the coefficients we need to write the charge per unit police. For example, if we are told that a reaction is second gild in A we know that n is equal to two in the rate law.
Top
Determining Exponents for a Rate Law from Initial Rates (Experimental Data)
If nosotros are given data from two or more experiments at the same temperature with different concentrations of reactants and dissimilar rates we tin can decide the exponents in the differential rate law for the reaction as follows:
- Write the rate law with the concentrations of all species for which information is given. Write the coefficients as unknowns: n, m, etc. For example, we might have an equation such as the following:
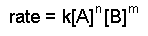
- Have ratios of the experimental data that give dissimilar rates.
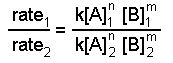
- Cancel common terms and solve for the exponent that does not cancel.
Example
If we have the following experimental initial rate data for the reaction
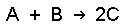
experiment [A], K [B], M rate = -d[A]/dt, M h -1 ane 0.l 0.fifty i.2 2 1.0 0.50 4.8 3 2.0 1.0 38.iv We tin write ratios for the data from experiments 1 and two
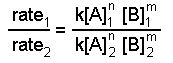
Using the data from experiments 1 and two, we come across that the k's abolish as do the concentrations of species B.
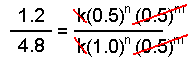
Solving this equation for northward yields n = 2.
At present we apply the known value of northward and information from experiments 1 and 3 or from experiments two and three and solve for thousand. Hither we use experiments 1 and 3:
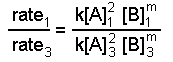
When we substitute the information we go:
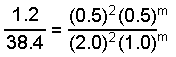
Solution of this equation gives g = i and the rate police force tin exist written:
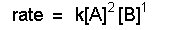
Meridian
Determining k, the Rate Constant
We can make up one's mind a rate constant from a differential rate law by substituting a rate and the respective concentrations (for instance, information from any of the experiments above) into a charge per unit police and solving for m. Using the data from experiments 1, ii, or three we could solve the following equation for k:
Elevation

Source: https://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/howtosolveit/Kinetics/DifferentialRateLaws.html
Posted by: burnerhimusince1972.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find K Constant In Rate Law"
Post a Comment